
The Goiás State Department of Health (SES-GO) has issued a technical note and implemented trainings targeting health professionals, from the public and private network, to guide the implementation of protection and control measures for the transmission of monkeypox, a disease known as monkeypox. smallpox.
Through Technical Note No. 12, symptoms, forms of transmission, definition of cases and measures to be taken in case of suspected, probable and confirmed cases of monkeypox in the country are defined.
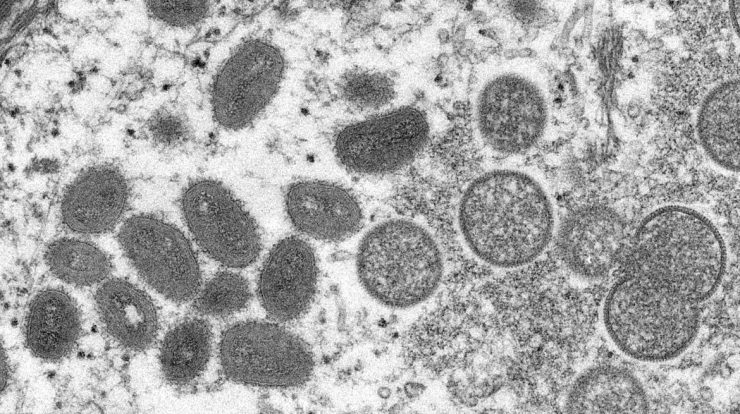
The disease is a form of smallpox, first discovered in the UK, and can be transmitted through personal contact, or with human body material contaminated with the virus. It is important to stress that monkeys are victims of disease just like humans. The epidemiological scenario of monkeypox is dynamic, with periodic updates by the team that makes up the operating room of the Ministry of Health.
As of Thursday (7/7), Brazil recorded 142 confirmed cases. Goias continues to investigate six suspected cases. The data is published from notifications provided by the country’s health services, through RedCap and the analyzes can be accessed through the link: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/composicao/svs/resposta-a-Emergency/ health-status-room / Monkeypox-case-room / update-of-cases-in-Brazil.
The state of Goiás also provides epidemiological information about the disease using the field for reports through the link https://www.saude.go.gov.br/boletins-informes
exercise
Two training courses targeting health professionals from the public and private network have already been carried out. The objective is to impart adequate information about clinical management in diagnosis and therapeutic management, and to enhance the medicines needed in treatment.
The first training, which took place on June 20, was attended by 88 specialists in a seminar. On June 28, 147 professionals from 54 municipalities were trained in another activity. The training is conducted online and will be made available on the SES-GO website for a permanent update of any health professional in the state. SES-GO has a dedicated technical group on call 24 hours a day, seven days a week, designed to support health professionals and municipalities in investigating and monitoring monkeypox cases in the state.
how to prevent
Between humans, monkeypox transmission occurs through contact with bodily fluids, lesions on the skin or mucous membranes, such as the mouth or throat, respiratory droplets during prolonged personal contact and through contaminated objects. Respiratory droplet transmission often requires long-term personal contact, putting health care workers, family members, and other people in close contact with infected people at greater risk.
Symptoms include fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, back pain, muscle aches, chills, and fatigue. Monkeypox is usually a spontaneous disease with symptoms lasting two to four weeks, referred to as skin lesions. The transmission period of the disease ends when the scales of the pests disappear. The incubation period ranges from six to 16 days, but can be up to 21 days.
Because it is contagious, the disease requires care to identify patients, isolate, report cases, lab tests, and monitor contacts. Treatment is based on supportive measures aimed at relieving symptoms, preventing and treating complications, and avoiding consequences.
serious cases
Severe cases occur more commonly in children and are related to exposure to the virus, the patient’s health, and the nature of complications. Underlying immune deficiencies can lead to worse outcomes.
Complications can include secondary infection, bronchopneumonia, sepsis, encephalitis, and corneal infection with consequent vision loss. Historically, the mortality rate ranged from 0 to 11% in the general population and was higher among children. Recently, the mortality rate was about 3%.
Check out Technical Note 12 in full here.
Text: Iara Lourenço from Telecom
Photo: EBC

“Friendly zombie guru. Avid pop culture scholar. Freelance travel geek. Wannabe troublemaker. Coffee specialist.”