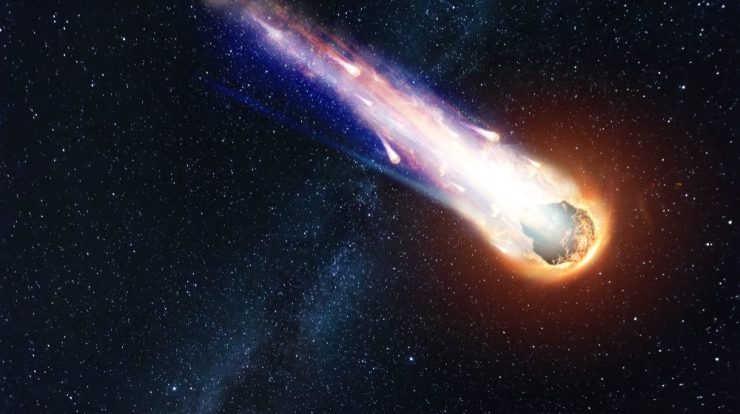
A very curious event happened in Solar System: A strange volcanic comet has violently erupted and released more than a million tons of gas, ice and “potential building blocks of life”. Known as 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann, the comet is about 60 kilometers across and takes about 15 years to orbit the sun. Sun🇧🇷
Researchers believe that these are the most “volcanically” active comets in the solar system. In addition, it is one of 100 comets, known as “centaurs”, ejected from the Kuiper Belt located in the outer solar system.
publicity
It was the amateur astronomer Patrick Wiggins who noticed the dramatic change in the comet’s brightness. Other observers also noted this increase in brightness and classified it as the result of a huge volcanic eruption. According to the British Astronomical Society (BAA), this was the second largest eruption this comet has seen in the past 12 years. The biggest event will happen in September 2021.
Read more:
Kay Stoddard-Jones, a PhD candidate at Cardiff University in the UK, told L.L.C Science lives that an eruption of this magnitude “is very rare.” He also noted the difficulty in measuring and explaining the dimensions of this type of phenomenon.
This unusual type of volcanic activity is known as an ice volcano, or “cold volcano”. Over time, radiation from the Sun can cause the icy interiors of comets to sublimate, that is, to transition from a solid state to a gas, causing pressure to build up under the crust. This pressure causes the outer shell to crack and the cryomagma, composed mostly of carbon monoxide and nitrogen gas as well as some icy solids and liquid hydrocarbons, hurtles into space.

NASA representatives point to the planet-forming potential of these debris ejected from comets, because the elements that make them up are the same ones that scientists believe gave rise to the planets of the solar system.
This unusual type of volcanic activity is known as an ice volcano, or “cold volcano”. Over time, radiation from the Sun can cause the icy interiors of comets to sublimate, that is, to transition from a solid state to a gas, causing pressure to build up under the crust. This pressure causes the outer shell to crack and the cryomagma, composed mostly of carbon monoxide and nitrogen gas, as well as some icy solids and liquid hydrocarbons, hurtles into space.
Have you seen the new videos on YouTube digital outlook? Subscribe in the channel!

“Friendly zombie guru. Avid pop culture scholar. Freelance travel geek. Wannabe troublemaker. Coffee specialist.”