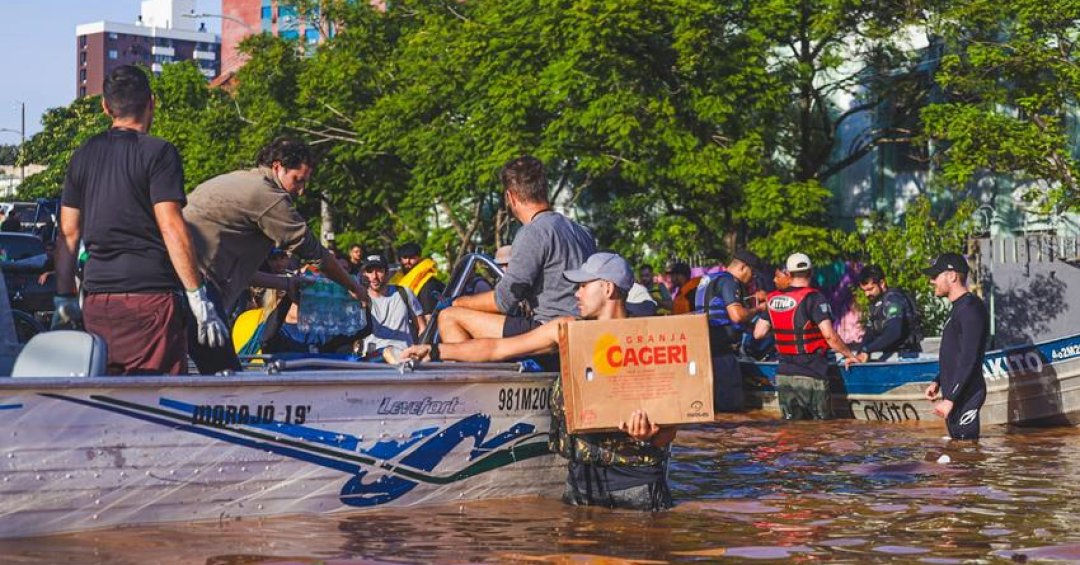
Given the talk Floods in Rio Grande do Sul The resulting increase in the risk of transmission of infection LeptospirosisIt is crucial to understand and adopt appropriate preventive measures – used to prevent diseases -. In a joint technical note dated May 6, the Brazilian and Gaucho Infectious Disease Societies, as well as the State Ministry of Health of Republika Srpska, issued Indications for chemoprevention Against disease.
Chemoprevention is understood as Preventive use of medications Before becoming infected or trying to prevent an already infected person from getting the disease.
Leptospirosis, an infectious disease caused by bacteria LeptospiraIt is most often contracted through contact with water or soil contaminated with the urine of infected animals, usually mice.
+Read also: Floods in Republika Srpska: What to know about leptospirosis and other flood diseases
Chemoprevention in leptospirosis
Infectious disease specialists point out that the routine use of prophylactic antimicrobials is not recommended. However, in high-risk situations, such as those that occurred during and after floods, Chemoprevention may be considered for certain groups.
According to a technical note released this week, this includes Rescue teams and people with prolonged exposure to contaminated waterLike a stranded person.
It is worth noting that leptospirosis does not always develop immediately after contact with contaminated water, as infection occurs in some cases weeks after the original infection.
To carry out chemoprophylaxis, Doxycycline is indicated as the main optionIn specific doses for adults and children.
For people in High risk after exposureThe recommended dose is 200 mg given orally as a single dose. to Adults who are in situations of continuous exposuresuch as rescuers or first responders, the dose is 200 mg orally once a week for the duration of exposure.
is for Children at risk after exposureThe dose is 4 mg per kilogram of body weight, given orally as a single dose, and the maximum dose is 200 mg.
Instead, the Azithromycin Can also be used. People at high post-exposure risk should receive a single dose of 500 mg orally.
For adults with continuous exposure, the dose is 500 mg orally once a week.
For children at high post-exposure risk, the single dose is 10 mg per kilogram of body weight orally, with a maximum dose of 500 mg.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) remains essential
It is important to remember that even with the use of chemoprophylaxis, There is no guarantee that infection will be prevented. Therefore, it is necessary, when possible, to adopt other preventive measures, such as the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) when in contact with contaminated water.
First, PPE protects against pathogens found in the water, e.g Bacteria, viruses and parasites, reducing the risk of infection. In addition, they help prevent skin injuries caused by irritating chemicals or sharp objects.
+Read also: Floods increase the risk of disease; What are the symptoms and care
Another important point is that personal protective equipment contributes to reducing the risk of cross-contamination. Prevent pathogens from spreading to other areas or people. This is especially important in work or community settings.
The appropriate use of personal protective equipment also enhances occupational safety in disaster situations. In rescue, cleanup and reconstruction operations, conditions can be dangerous, and PPE helps ensure the safety of workers involved in these activities.
When returning home after flood events, the risk of infection remains high, requiring continued use of personal protective equipment when possible. Adopt strict hygiene measures.
Share this article via:

“Friendly zombie guru. Avid pop culture scholar. Freelance travel geek. Wannabe troublemaker. Coffee specialist.”