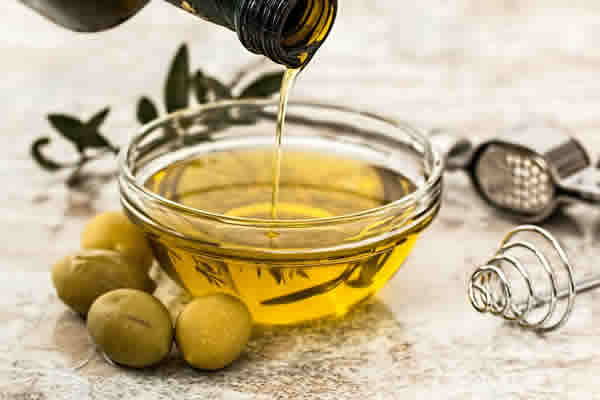
The history of olive oil dates back thousands of years, and evidence of its use dates back to ancient times. In addition to being a staple of the Mediterranean diet, olive oil was used to relieve pain and treat injuries in ancient warfare. Its benefits extend beyond the culinary field, with properties that contribute to the overall health of the body.
There are several types of olive oil available for consumption, each with unique properties. For example, extra virgin olive oil is considered the healthiest, with a distinct flavor and aroma.
Virgo, although sharing similar benefits, may have a slightly higher acidity.
Meanwhile, refined olive oil, although it retains some Fatty acidsIt may lose part of its properties during the refining process. Finally, olive oil is a mixture of refined and virgin or soybean oil.
The nutritional properties of olive oil are remarkable, as it contains monounsaturated fats, omega-9, vitamins E, A and K, in addition to minerals such as iron, calcium and potassium. Its antioxidant compounds are particularly beneficial, providing a series of health benefits.
One of the most important benefits of eating olive oil regularly is its ability to fight infections. Studies show that extra virgin olive oil contains natural anti-inflammatory compounds that can provide relief from chronic pain, comparable to the effectiveness of medications such as ibuprofen.
In addition, olive oil is known for its role in promoting cardiovascular health. Monounsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols contribute to reducing bad cholesterol and preventing heart disease, as comprehensive research has shown.
Other benefits include protecting the brain from oxidative stress, improving symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, strengthening bones, and even reducing the risk of depression.
Although studies are still ongoing, there is promising evidence to suggest that olive oil may help prevent neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and even protect against certain types of cancer.
When it comes to olive oil consumption, moderation is key. It is not recommended to eat more than two tablespoons per day, preferably in its unheated form to preserve its antioxidant properties.
When purchasing, it is important to choose pure olive oil, packaged in dark containers to protect from light. With many proven benefits, olive oil remains a healthy and versatile choice for cooking and health promotion.
Source: Guia Muriaé, with information from Viva Bem/UOL

“Friendly zombie guru. Avid pop culture scholar. Freelance travel geek. Wannabe troublemaker. Coffee specialist.”