The problem may increase the risk of heart disease and anxiety
iStock

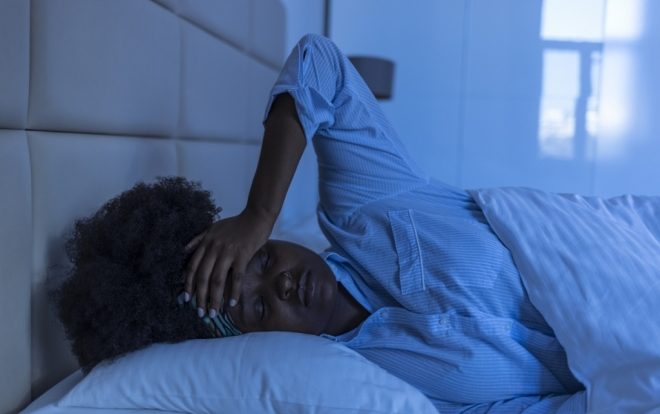
Did you know that you can make up for the few hours of sleep per week on Saturday and Sunday? This procedure, practiced by people who spend a very busy week and cannot get enough sleep each day, can cause a sensation similar to the fatigue of long flights.
The body begins to get confused about when to sleep, eat, or even do physiological needs, all because of the time zone that tends to change from place to place on long, transcontinental flights. A similar sensation can be experienced by people who do not sleep regularly.
Social jet Lag: What is it?
Interruptions in sleep patterns can cause a person’s biological clock to falter. This results in a series of consequences, such as metabolic dysfunction, diabetes, obesity and mental illness.
Jet lag is measured by a simple calculation that determines a person’s mid-sleep. Suppose a person sleeps from midnight until 8 am, in this scenario the midpoint of sleep is 4 am. On weekends, this person sleeps from 2 am until noon, so the midpoint becomes 7 am. Therefore, the social travel delay for this person would be three hours, because 7 – 4 = 3.
health complications
According to research published in the journal Sleep, for every hour you experience more jet lag, there is an 11% increase in your likelihood of developing some form of heart complication.
Other research, published in the International Journal of Obesity in 2015, found that “living against our internal clock can contribute to metabolic dysfunction,” so increased differences in sleep patterns (such as two hours) could significantly increase risk.
Mental health is also completely affected, especially if we consider that a person who is not able to maintain a healthy sleep routine can suffer from significant stress and signs of fatigue. A UK study published in Nature, with more than 85,000 people, found that people with jet lag had a significant increase in anxiety, which can lead to depression.
According to Christina Salles, “Research shows that long-term sleep deprivation contributes to emotional vulnerability and even to the development of mental disorders.” Christina is in charge of the Sleep Medicine Service at Professor Edgard Santos University Hospital, UFBA (Federal University of Bahia).
Solve the problem
To reduce social travel fatigue, ideally, you should maintain a regular sleep pattern. Always try to go to bed and wake up at the same times, and maintain a consistent and relaxing routine as much as possible. Include physical exercise in your routine, even if it’s just a walk outside once a day.
Consultation with doctors and professionals trained in Nursing School A thorough examination can also be necessary to find out the state of your health.

“Friendly zombie guru. Avid pop culture scholar. Freelance travel geek. Wannabe troublemaker. Coffee specialist.”