The past few days have been rocked by a Russian military operation in Ukraine – and in some way this has been reflected in space exploration. The crisis puts Russia and the United States in a political and diplomatic conflict, which could jeopardize the future of the International Space Station, which is primarily led by the two powers.
Despite this, other fascinating discoveries have appeared in astronomy news in the past week. Check out the most important ones below!

Asteroid 1999 VF22 approached its closest point to Earth in a century last Monday (21), and it was accompanied by a live broadcast. Although potentially dangerous, there was no danger of it colliding with our planet, as the space rock was at a distance of 14 times the distance from Earth and the Moon.
Want to stay up to date with the latest tech news of the day? Access and subscribe to our new YouTube channel, Canaltech News. Every day a summary of the most important news from the world of technology for you!
The object passed through Earth’s orbit at a speed of 25.1 km / s, and will not return to our ocean until February 23, 2150. Direct transmission was made by the Virtual Telescope Project.
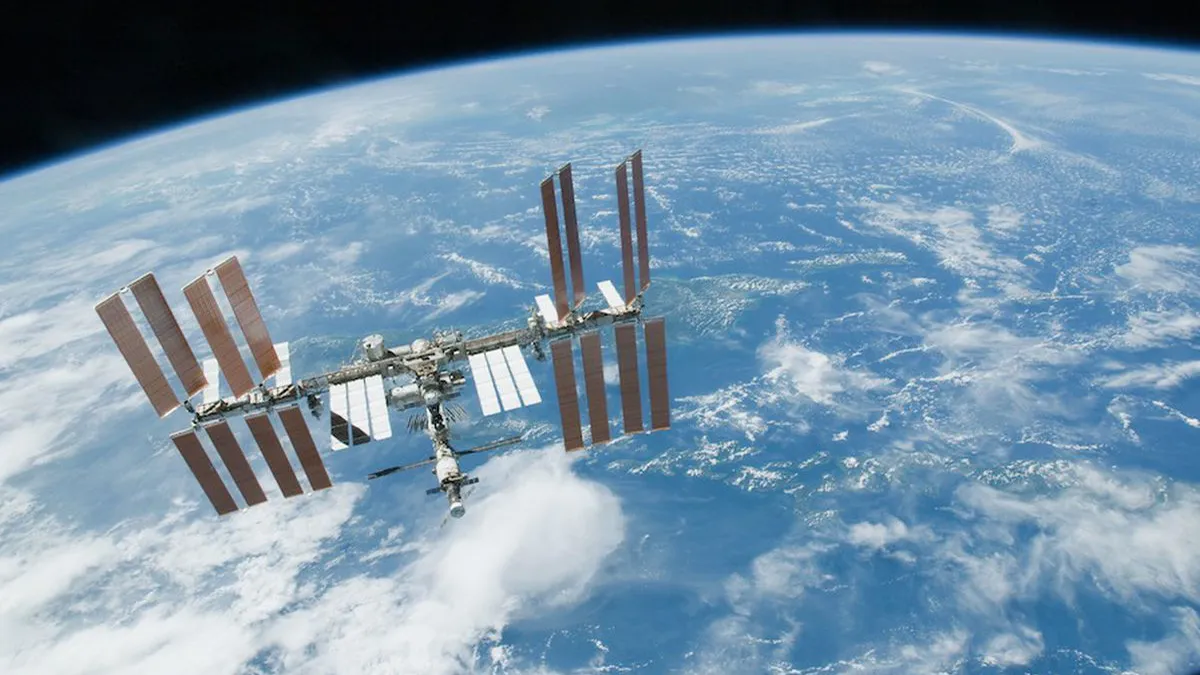

It appears that the Russian military operation in Ukraine could lead to serious consequences for the International Space Station (ISS), which is maintained by the joint work of NASA and the Russian space agency Roscosmos. After the US President announced the harsh sanctions he imposed on Putin, Roscosmos Director Dmitry Rogozin published a series of tweets containing clear threats.
Rogozin’s main message is that sanctions can put an end to the partnership between the two agencies. In doing so, the International Space Station could end up “falling off” in undesirable places…such as US territory. The message is not without its foundation: Roscosmos is responsible for correcting the station’s orbit, which must be done repeatedly so that it does not re-enter the atmosphere.
Without the cooperation of Roscosmos, the International Space Station could crash into this planet and, even worse, somewhere populated. Rogozin argued that the United States should carefully assess the political situation lest it become responsible for such a catastrophe.

According to Wang Wenbin, China’s foreign minister, the fall stage of an old rocket on its way to colliding with the moon does not belong to the vehicle used to launch the Chang’e 5 T1 mission. Previously, data indicated that the object could be part of Falcon 9, from SpaceXbut soon after appeared to belong to China, according to new analyzes.
However, state monitoring shows that the upper stage of the Long March 3C rocket, which was used in 2015 on the Chang’e 5 mission, re-entered Earth’s atmosphere and was completely incinerated. Thus, the “identity” of the object bound for the moon remains unknown.

New images of the center of NGC 7582 reveal activity at the outskirts of a supermassive black hole. So far, nothing new – astronomers have already taken a huge amount of pictures of active galactic centers like this one. But what caught our eye this time is the presence of energy flows that have been redirected away from the rest of the galaxy by a “wind”.
This wind, which is actually only visible energy at a certain wavelength of light, pushes the violent outflows from the black hole away from the star-forming cloud. In other words, some mechanism seems to protect the “star nursery”, which would otherwise have been destroyed. Scientists still do not know what this mechanism is.
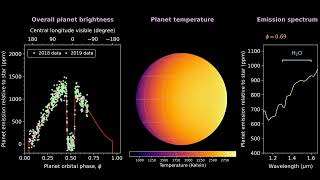
Exoplanet WASP-121b is not just a “hot Jupiter”, it is also a place dominated by two extremes: one side is always immersed in its star’s intense radiation and the other is engulfed in perpetual night. But even more amazing are the restrooms and their clouds.
The diurnal face of the planet is so hot that water molecules disintegrate, separating hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The wind then carries these atoms to the night side, where they cool down and return to water vapor. However, even the dark side is too hot to form clouds of water. On the other hand, high temperatures form clouds of minerals and minerals resembling liquid sapphire and sapphire.

The Yutu-2 rover from China found small balls of transparent glass in dust on the far side of the Moon, and this glass may have formed from the intense heat of a meteor impact, or even from ancient volcanic activities.
This is not the first time that globules have been found on the surface of the Moon, for example, astronauts on the Apollo 16 mission found some as large as 40 mm.
