Climate extremes that occur in the Amazon rainforest directly affect those that occur in the Tibetan Plateau, according to research by scientists.
The Himalayas, a vital region for securing water supplies for millions of people, are close to it Potentially catastrophic “tipping point”.Also, these scientists warned.
in Climate change Caused by human activities, critical ecosystems and entire regions lead to often irreversible changes.
Among the areas particularly vulnerable to these climatic disturbances icy peaks Which, if melted, could cause sea levels to rise by several metres.
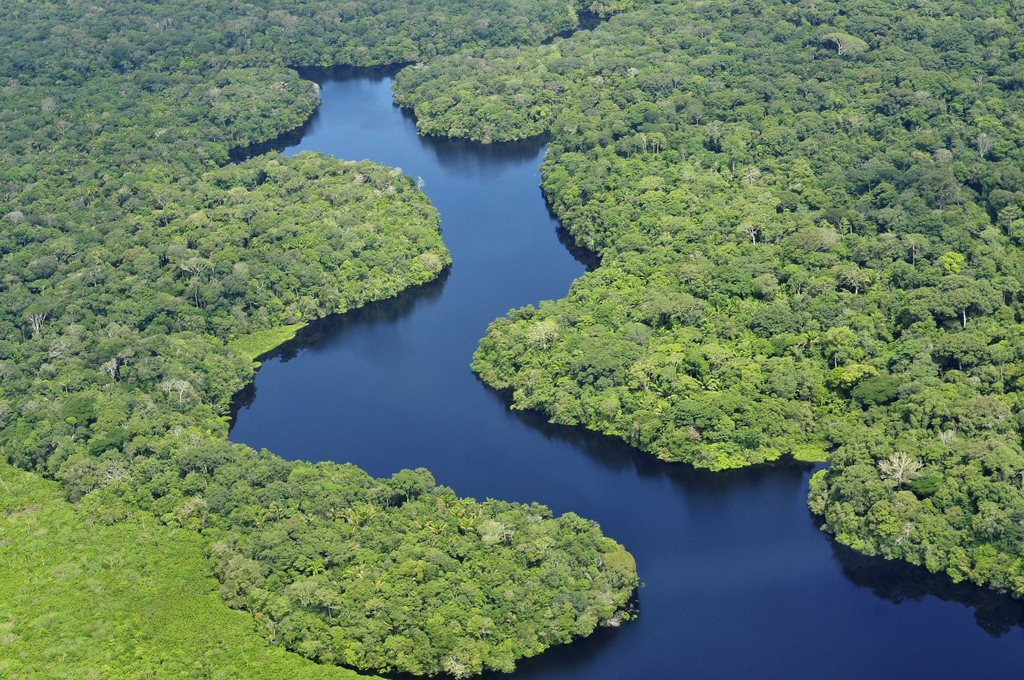
In the Amazon basin, it is found Tropical flowers victims Elimination of Forests risk turn into a savannahwhich will prevent them from fulfilling their role as carbon sinks on the planet.
But could a “tipping point” in one part of the world have a domino effect in another? This is exactly what recent research suggests.
Heat in the Amazon raises temperatures in Tibet
in Climate change in the Amazon basin has implications for the Tibetan plateaulocated 20,000 km away, included Chinese, European and Israeli scientists, in an article published in the journal NatureClimate Change. Climate change.
Scientists used data from around the world near-surface temperatures Over the past 40 years to discover the climatic links, from South America to South Africa and the Middle East, and finally to the Tibetan Plateau.
Computer simulations were then used to determine how to use Global Warming These links can be changed in the long run, up to 2100.
Since then, scientists have found it When the temperature rises in the Amazonin Temperatures are also rising in Tibet.
However, on the contrary, when The rain is getting worse In the rainforests of South America, the Snowfall is decreasing The Himalayan region is sometimes referred to as the “Third Pole”.
The domino effect is very risky
Scientists talk about it “remote communication”But they stayedSurprised To find out how climate extremes in the Amazon region are closely related to climate extremes in Tibet,” postulates the co-author of the study, Jürgen Kurths, of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) in Germany, in remarks quoted in the official statement on the study published by the website. EurekaAlert!
The researchers analyzed changes in air temperature near the surface in Network of more than 65,000 sub-districtswhich considers nodes, which were placed on the globe, using data from the past 40 years,” it was explained in the statement.
In this way they achievedSee how changes in one node affected those in another nodeAnd it discovered “a clear dispersal path over more than 20,000 km – from South America, through South Africa, to the Middle East, and finally to the Tibetan Plateau,” the PIK statement confirms.
Research also highlights this “Tipping Falls” is a risk that must be taken seriously: the interconnected displacement elements of the Earth system can run into each other, with Serious consequencesAnother co-author of the study, Hans-Joachim Schellnhuber, also from PIK, points out.
“It is very unlikely that the climate system as a whole will change,” Schellnhuber adds. However, with the passage of time, the Subcontinental tilt events It can seriously affect entire communities and threaten important parts of the biosphere,” explains the researcher.
And “This is a risk we must avoid.”He also warns, stressing that we can do this by “rapidly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and developing nature-based solutions to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.”

“Proud explorer. Freelance social media expert. Problem solver. Gamer.”